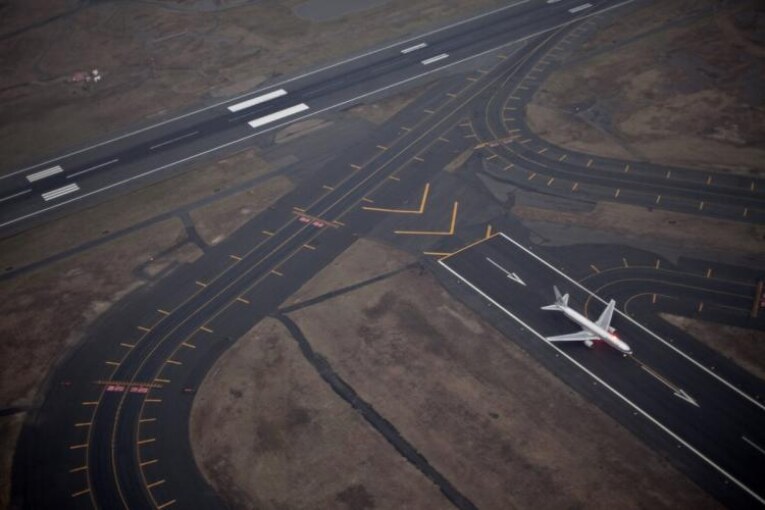

Runway
- “Rectangular area on an aerodrome used for landing and takeoff.”
- Runway orientation is important in airport planning.
- Current practice is to layout a runway in the direction of prevailing wind.
Importance of runway layout
- Determination of runway is a critical task.
- It is very important for safe take offs and approaches.
- The width and sloping of runway also play a role in safe approaches.
Runway Numbers
- Runways are numbered according the magnetic compass direction.
- Consists of two numbers one at each end of runway.
- Preceding that number are eight stripes.
Runway Heading
- By 500 feet is the touchdown zone, identified by six stripes.
- Runway numbers are not given in degrees, rather in shorthand format.
- g. a runway with a marking of 14 is actually 140 degrees.
- For simplicity FAA rounds off the precise headings to nearest tens.
Runway Configuration
- FAA includes over 20 runway layouts.
- Amongst them there are 4 basic runway patterns:
- Single Runway
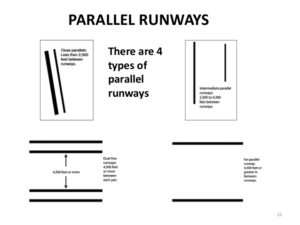
- Parallel Runway
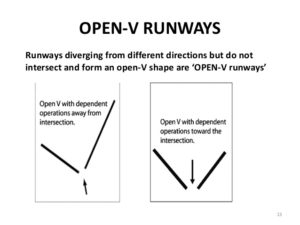
- Open-V Runway
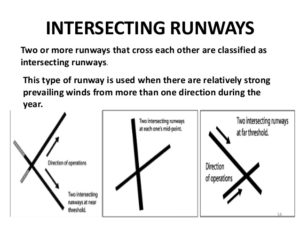
- Intersecting Runway
Single runway

Parallel runway
Open-V runway
Intersecting runway
Factors affecting runway orientation
- Wind
- Airspace Availability
- Environmental factors
- Obstructions to navigation
- Air traffic control visibility
- Wild life hazards
- Terrain and soil consideration
Wind rose analysis
- An approach often used in determining the runway orientation.
- The method uses a wind rose template.
- A transparent runway template is placed and rotated around the center of wind rose.
- At each rotating angle, the percentage of allowable cross winds is measured.
Runway Lighting
- These lights are used to assist pilot in to identify the runway.
- Green Threshold Lights: Line the runway edge.
- Red Lights: Mark the end of runway.
- Blue Lights: Run alongside taxiways.
- While runways have Yellow or White lights marking their edges.
Runway Signs
- Various kinds of runway signs are also used for facilitation.
- They differ according to their purpose and action.


