Introduction
- Whenever there is an earthquake related disaster in the news with collapsed buildings & other structure all over the place, one may think that earthquake resistant design of structure are still in dark age. Thus we desperately need advanced earthquake resistant design to make structure less vulnerable to earthquake even for large earthquake.
What is an Earthquake??
- They are natural disasters of a generally unpredictable nature.
- An earthquake is the vibration of earth produced by the rapid release of accumulated energy in elastically strained rocks.
- It is the shaking of earth due to the movement of earth’s crust.
- Energy released radiates in all directions from its source, the focus.
- Energy propagates in the form of seismic waves.
- A sudden, rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rocks beneath the earth surface.
- Sensitive instruments around the world record the event.
How Earthquake Occurs??
- Because of Earth’s rotation and other energy factors different shells or the rock layers constantly move or slid past each other.
- Different continental mass fragments of lesser densities float and move overriding the denser rock layers.
What causes an earthquake??
- Movement of Tectonic Plates: Earth is divided into sections called tectonic plates that float on the fluid-like interior of the earth. Earthquakes are usually caused by sudden movement of earth plates.
- Rupture of rocks along a fault: Faults are localized areas of weakness in the surface of the Earth, sometimes the plate boundary itself.
How Earthquake Causes Damage
- The severe shaking produced by seismic waves can damage or destroy building & bridges, topple utility poles & fracture gas and water mains.
- S wave can put stress on building to tear them apart. Also trigger landslide or avalanches.
Effects of Earthquake
- Ground motion
- Landslides
- Ground displacement
- Liquefaction
- Tsunamis
- Aftershocks
Construction Methods
- Base-isolated are designed in buildings. It is a building designed to reduce amount of energy that reaches the building during earthquake.
- Flexible joints and automatic shut off valves can be installed.
Quality Control
- Special care is needed in construction to ensure that the elements meant to be ductile are indeed provided with features that give adequate ductility.
- Thus, strict adherence to prescribed standards of construction materials and construction processes is essential in assuring an earthquake-resistant building.
Elements of Good Quality Control
- Regular testing of construction materials at qualified laboratories.
- Periodic training of workman at professional training houses.
- On-site evaluation of the technical work.
Earthquake resisting structures techniques
- Base isolation method
- Energy dissipation device
- Keeping building up thrust
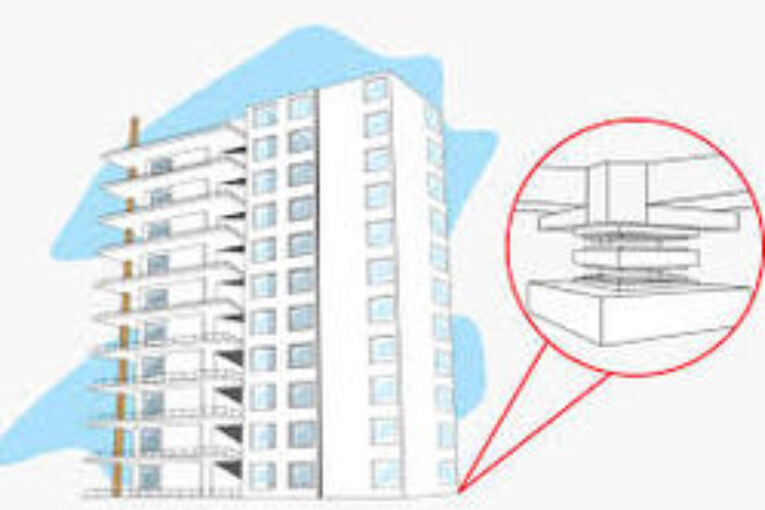
Base Isolation
- Introduces flexibility to the structures.
- Building is rested on flexible pads.
- When earthquake strikes the building does not moves.
- It is suitable for hard soil only.
Energy Dissipation Device (Seismic Dampers)
- These are used in place of structural elements such as diagonal braces.
- Acts like the hydraulic shock absorbers in cars.
- When seismic energy is transmitted through them, dampers absorb part of it, and thus damp the motion of the building.
1. Viscous Dampers
2. Friction Dampers
3. Yielding Dampers
4. Viscoelastic Dampers
Keeping building up-right
- Recently discovered technique of Japan.
- It has found to be survived even in extreme earthquakes.
Conclusion
- In the coming years the work in the field of EQRD is very important to have safe structures which can take the effect of earthquake with less damage to the society.


